 |
| Image Courtesy: Canva.com |
Ever wondered how when you google something, Google presents you with millions of results in less than one second?
Doesn’t that sound impossible? How could Google or any search engine search through the entire internet to find the most relevant result for you and a few billion other people every day?
The answer is it doesn’t!
It does not scan the world wide web as and when you search! Sounds confusing?
Read on to know:
1. The Basic Search Landscape; How a normal search result looks like.
2. How do Search Engines work?
3. Crawling
4. Indexing
5. Ranking; and everything in between!
The Basic Search Landscape: How a
default search result looks like
This is how a normal search result looks like. It has
three main elements:
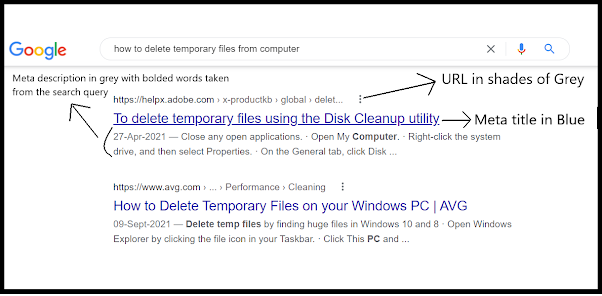
1. The URL on top in a combination of dark grey and light grey ;
2. The
Title in middle in Blue;
3. And,
the description below in dark grey.
Although there are many different types of search
results that Google shows up depending upon the search query; Images, Videos,
featured snippets, rich results for instance; but we will talk about it in another blog.
Here, we are trying to understand what Google takes from a web page on the
internet to show on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
The basic search snippet that is taken from a web page
leads us to conclude that the three elements are of prime importance for both,
the search engines primarily and the users.
Because as users, we see the snippets on the results
page and decide with a naked-eye scan which result is to be clicked.
From the point of view of SEO, we have to consider
this to make our web pages search engine friendly.
If you are looking for a basic guide to Search Engine
Optimization, click here to read our detailed blog on the basics of SEO and how is it important for marketers.
Coming back to understanding how Search Engines work,
we come up with the question, how does Google look into the web pages and store
this information to show on the search engine results page.
Google or any Search Engine for that matter go through
several steps before we see the beautifully designed Search Engine Results Pages.
How do Search Engines
work: Crawling
 |
| Representational image of a web crawler/spider/bots from canva.com |
By definition, Search Engines are software programs
backed by Algorithms to crawl (search through) the world wide web, index it
(store in the servers) and rank the indexed results in the order of highest to
lowest levels of relevance to the search query.
Crawling is done by the web crawlers or otherwise
known as spiders, bots (as in robots). These are software programs that explore
the web 24 by 7 by 365 following links after links, websites after websites.
It is the way Google gets to know about the new
websites coming into existence and how older ones are changing.
The frequency of the crawling depends upon many
factors, like how old your website is, how often your website is updated, how
many visitors visit the website, and basically, how important your website is
from the point of view of other websites.
If your website is new, it might have to be submitted
to a Search engine webmaster tool, Google Search Console for instance is the
webmaster tool by Google.
Submitting the website for crawling and indexing helps
search engines know about your website in a faster way than it would have
happened organically.
How do Search Engines work:
Indexing
 |
| Representational image of search engine indexes from canva.com |
After a web crawler or spider goes through a (web)
page, it decides if a web page is relevant to be indexed or not.
By index, it means to download a copy of the web page
and everything which is there on the web page; images, videos, pdfs, white
papers etc. and then store it in a particular database where the search engine
finds it suitable.
Say, this web page you are reading might be
indexed in the database of other pages which provide a similar type of
information, that is, information about how Google search works or how Search
Engines show results.
The results that we see on a search results page are
the ones that were indexed previously and downloaded in the search engines’ servers.
As Search Engine Optimizers/website owners, it is important
to ensure that the web pages of your websites are indexed by the Search Engines
without which they will not appear in the search results, even if you search
using the domain name of the website.
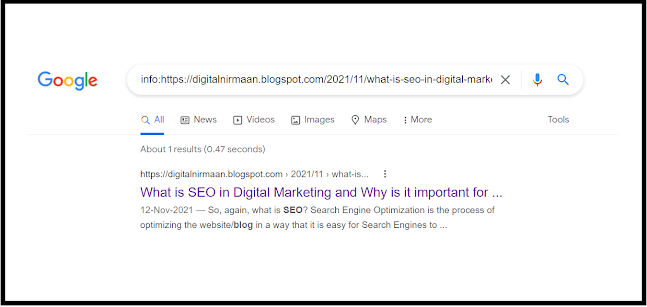
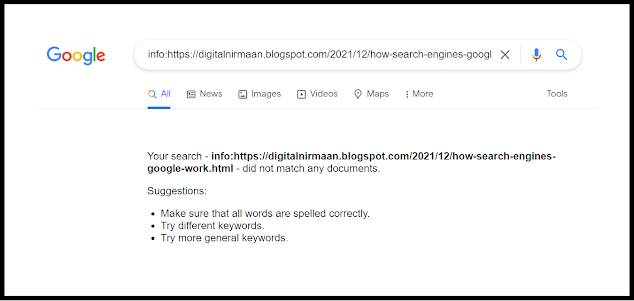
To check if a web page is indexed or not, search "info:URL of the web page". If it appears in the search result, as shown above, it is indexed. If it is not indexed, it will show a 404 error or Page not found error like this 👇
In case it is not indexed, you can manually place an index request on the Google Search Console through "URL inspection > Request Indexing". It will most probably be indexed in 24-72 hours.
How do Search Engines work: Ranking
 |
| Representational image of Ranking web pages by google from canva.com |
It is said that Google Algorithm takes into account
more than 200 factors to decide the rankings of the indexed web pages.
The most common factors that are estimated and those work for the majority of the websites are:
· Relevancy:
How relevant is a web page according to the search query? Will it be sufficient to answer the searcher’s query? Analyzing what users’ search to find what your business sells and creating a useful and information-rich website should be on top of your list.
On-Page optimization:
I have already talked
about the basics of SEO in this blog where I mentioned how Search Engines see
HTML instead of catchy fonts and images which we can see. To reiterate briefly,
Keywords and links are the roots of optimization. Ensure mentioning the
keywords that you found in the keyword research process in all important places
of the web page, especially the three we discussed above.
· Links:
Search Engines discover
new web pages through links. They follow links from known web pages to other
web pages linked from them.
It is a great help for
Search Engines if your website can be reached through other websites. It can be
a bit difficult when you start but goes a long way if you can get some good
quality links (from good websites)
· Avoid wooing Search Engines:
We don’t live in the
early 2000s where stuffing keywords everywhere on the page would make you rank
on the first page.
Search Engines are now backed by artificial intelligence which is learning NLP (Natural Language processing), trying to learn the natural flow of language just like humans do. As humans won't like content where the natural flow of language is compromised, search engines also do not like it.
Search Engines have
been and continue to improve to show the best results to maintain their market
share. So, are we supposed to learn all the updates on how search engines work
and show results?
I think not. Just
knowing the basics we talked about will suffice. The closer we are to
anticipating the needs of users, the better we can work on creating a
user-friendly experience. And just doing that much, I believe that the Search
Engines will find your website useful.
If you have any questions, feel free to drop them in the comments below or reach me out through the contact us form embedded in the sidebar.
A friend might need this information, share it.
You think I should improve somewhere; you can mention that in the comments too.
I am Pawan! Thank you for reading!


0 Comments