 |
| Image attribution: create.vista.com |
Do you know as you read this, approximately 4 million other people are searching on Google or at any given minute of the day? That is more than 2 trillion searches per year.
What are
they searching for? They are searching for things they want to know, places
they want to go, products they want to buy or anything as simple as “how to
bake a cake at home?”
On the flip
side, there are those businesses that satisfy all of these questions. Isn’t it
a big opportunity? To be in a position to help those people and have all those business
opportunities that they bring.
A big reason
to be there online when someone searches for something YOU have is, it pays
nothing to be there.
In one of
my recent posts, I had talked about the basics of Search Engine Optimization
and how it is important for businesses. If you are a beginner at SEO, I would
recommend reading that first.
There I
also talked about the two types or two ways we can influence our rankings on
any Search Engine. These are:
- On-Page
optimization
- Off-page optimization
·
In this
blog, I will give you a complete On-page Optimization checklist that you can
use while optimizing your existing (web)pages and while creating new ones!
What is On-Page Optimization in SEO?
On-page
optimization is everything that you do on your website that influences your rankings
on the search engines.
On-page
optimization includes work to be done to woo both the searchers and the Search
Engines.
Google or
any search engine’s motive is to maintain their market share in their industry.
And to achieve that, they need to understand the searcher’s intent as
accurately as possible and show them the most relevant result on the internet
to satisfy their intent.
Understanding
how search engines work, we can work accordingly to provide for the searchers’
intent, thereby convincing the search engines simultaneously.
I know it is
easier said than done. Why? Because there are technicalities included.
Before we
talk about what techniques work in the On-page Optimization of a web page,
let’s first talk about what doesn’t work. It is more important, believe me!
The old school on-page SEO techniques that do not work today
Since the
introduction of major Google algorithm updates (Penguin, Panda and Hummingbird
updates), the following tactics do not hold much significance. Perhaps, using these,
again and again, might hamper your page quality and user experience, thereby
negatively affecting your search engine rankings. That is not what you would
aim to while doing on-page optimization of your web pages.
1. Stuffing exact match keywords repeatedly:
Google has become smart enough these days to understand the search
intent very accurately. It is powered by Rankbrain, the machine learning
algorithm that is learning 24 by 7 how searchers’ search.
It can easily look through the intent even when people do not search
with proper words, when they use synonyms or when they do not use normal
chronology of words.
Let me show you this by an example:
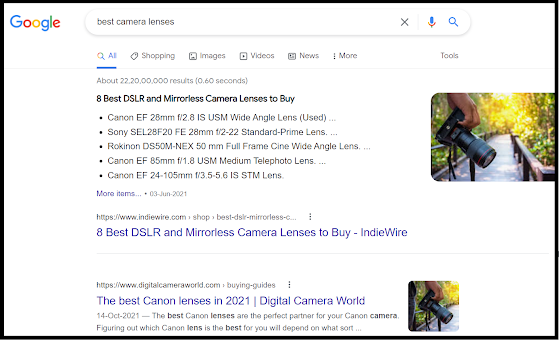
- Results when I search "Best Camera lenses":
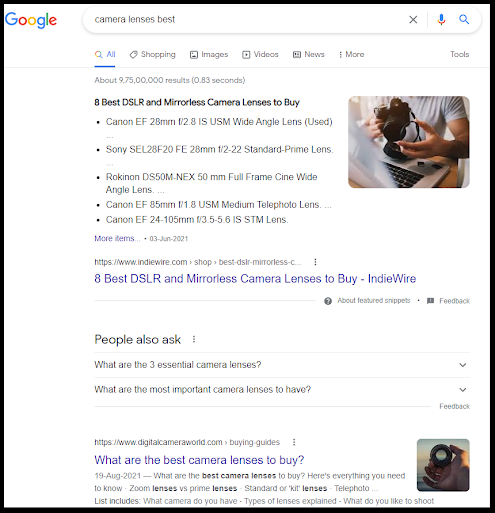
- Search results when I search "Camera best lenses" (Note that I changed the chronology of the words in the phrase)
- Search results when I search "lenses camera best"
No matter what sequence of words I use when searching for the ‘best camera lenses’, the results shown are more or less the same.
So, probably you do not need to focus on using the exact match keywords
everywhere in the body copy of the web page, compromising the natural flow of
content and user experience eventually.
2. Using the keywords, a particular number of times:
Online, you might come up with strategies that
tell you to include the primary keywords a certain number of times, which is
generally 2 to 5 per cent. But that is not sound advice again.
With the advancement of machine learning, we no
longer need to include the keywords, again and again, to tell search engines
that this is the word need to target.
Using them in certain important places is
sufficient enough to do the job (We will talk about these places in detail in
this blog, do not worry! 😊)
Let me show that again with an example.
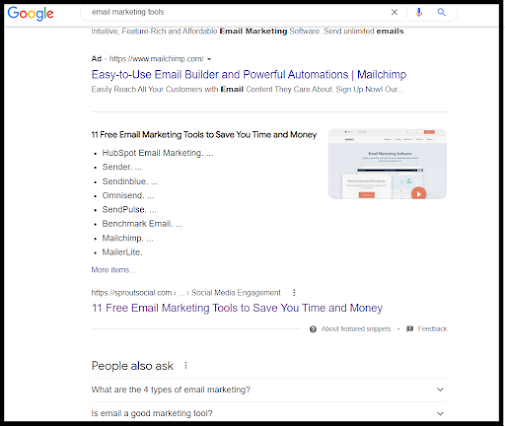
I searched ‘Email marketing tools’ on Google and clicked on the first organic result after the ads.
I then copied and pasted it into
a Word file. It turns out it is 1600+ words long and the expected primary keyword,
‘Email marketing tools’ appears 10 times which is less than 0.7 per cent of the
total word count. But still, it ranks number one (organically).
3. Meeting a minimum word count:
There have been some studies that point out
that the longer form of content ranks better.
Now, this is not totally wrong as the previous
two points. While stuffing keywords can up your spam score, meeting a certain
word count every time without the need may not help with your rankings.
Although said repeatedly, the key is to match
the searcher’s intent. Say, if what I search demands an immediate response,
something like today’s match live score.
Do you think I would like to read a 700-word
article to know that? No, right.
Rather, I don’t even need to click on any
website. It is shown on the results page itself.
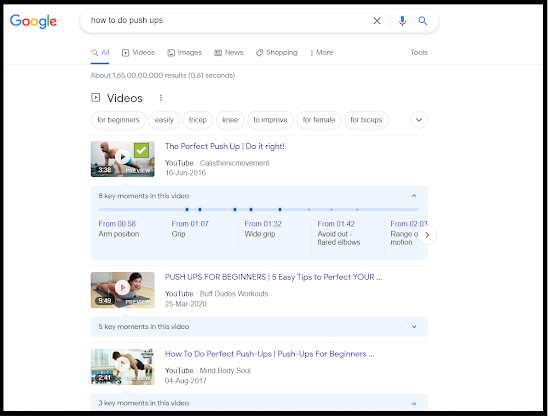
Another example of this would be; Say I want to
learn to do push-ups. The better content type would be a video and that only
ranks on number one.
No matter how many word long articles you
write, you cannot rank number one!
Again, MATCH SEARCHER’S INTENT. We need to
estimate what a searcher wants and how can we provide him with that.
Complete On-Page SEO checklist that works
Following
are the things that have been tried and tested by the pioneers of Search Engine
Optimization. These techniques are in complete sync with the Google webmaster
guidelines.
The first
one would be matching search intent. Your content should match the search intent
manifested in the keyword you choose. But, I have talked about it above, so, I
will not mention it down here.
1. Optimizing HTML Tags:
It has already been established here how search engines work. So, to
tell them what exactly our web page is all about, we need to optimize our web
page with a cluster of keywords (primary and secondary) in the different HTML
tags.
a. The URL/permalink/slug of the web page:
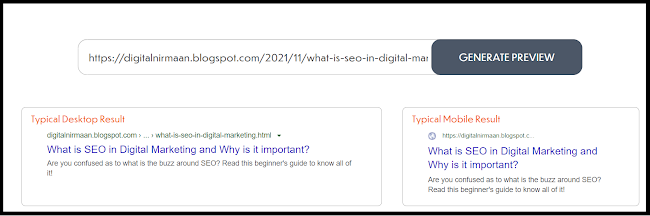
The slug is the part of the hyperlink that is after the domain name of the website. The slug of this page would be everything that is there, after the “https://digitalnirmaan.blogspot.com/2022/01/”, where 2022/01 is the time the blog is first published.
We need to put the primary keyword in the slug of the page. For eg: My primary keyword on this blog page is “On-Page SEO checklist”. Hence, the full URL is https://digitalnirmaan.blogspot.com/2022/01/complete-on-page-SEO-checklist/
You have full control over the URL settings of your website on any
modern CMS like WordPress, Wix, Shopify etc.
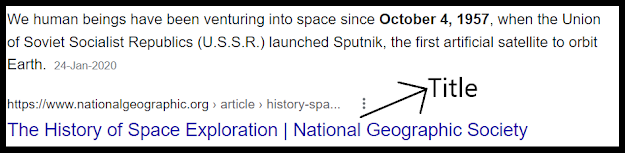
b. Title tag:
The title tag of any web page is what shows up on the Search Engines
results page.
It does not appear on your web page. Most of the time, it is similar to the <H1> tag (the heading tag) of the web page. On my page as well, I have kept the title tag the same as the H1 tag which is “Complete On-Page SEO checklist 2022: What works and what doesn’t?”
We have to place the primary keyword inside the Title tag as I have placed “On-Page SEO checklist” inside it.
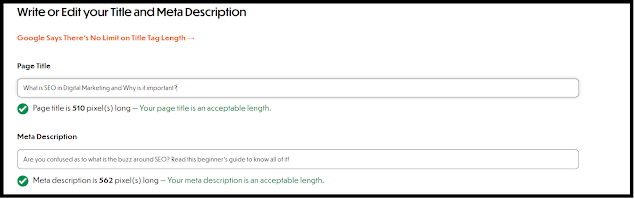
There is no perfect title length that should be followed as it depends
upon the pixel length and the device where the searcher is searching. A rough
idea would be it should be anywhere around 40 to 65 characters. Any more than
that would not appear on the SERP.
You can use a tool to check how would your title appear on https://totheweb.com/learning_center/tool-test-google-title-meta-description-lengths/
You can also experiment here as to what title would be a good length.
c. Heading tag
There are 6 types of Heading tags in HTML. From H1 to H6.
A page has only one H1 tag which is used for the heading of the page. The rest shall be for sub-headings and other minor headings.
The H1 tags should be used for the primary keyword as I did- “Complete On-Page SEO checklist 2022: What works and what doesn’t?”
The other tags H tags can have both primary and secondary keywords
and/or semantics (synonyms or related words of the topic).
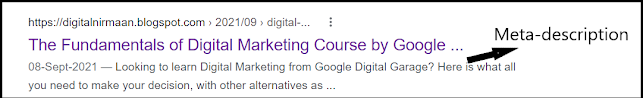
d. Meta-description tag:
You must have seen the short description of a search result on the
search engines results page! That is called the meta-description of the page.
We know how it works as a user. When we search for something on Google, we do a naked eye scan over the results page looking at all the descriptions of the search results. So, basically, it determines how many people will actually click on your search result.
Most of the time the meta description is changed according to the search
query. Google takes a relevant part of the page to show it to the user in case
the meta description tag that you have used, does not seem (to google) to
satisfy the search intent.
e. Image size and alt attribute
Images on your web page should be unique, compressed but of good quality (I will talk more about it in the later part of this blog). Secondly, there is an alt (as in alternate) tag that technically is used to aid the blind people who use screen readers to know what is there on the page but more importantly, Google also takes hints that the images used are of relevancy to the content on the page.
So, there are two reasons to use the alt attribute of the image.
First, for the blind people and second, for the hint for Google to know
the relevance. And for the second reason, we include the primary keyword in the
alt attribute.
See how I included the keyword in the alt text in the first image of this blog (the blog banner)
f. Paragraph tag:
A paragraph tag is normally the text/the body tag where you write the
content of the page.
In simple words, you should have all sorts of keywords in here, the
primary and the secondary ones, the synonyms and the related words.
2. Optimizing for User Experience
Among many other factors, the Google algorithm places much significance on the user experience part. There are hundreds of things that define how people experience your website. Let’s explore them:
a. Conversion friendly design
The design your web page has should be simple and user friendly. Placing too many calls to action could make the user leave your page for other websites.
The user should find what he needs without much effort. The fonts should
be different sizes.
The heading of the page is the largest text on the page followed by other sub-headings.
The psychology of colour should be taken into regard. You can read more about it here.
b. Readability
Readability is the ease with which the user is processing your content. It is easier to read short paragraphs as these instead of long paragraphs without any space in between.
Text in bullets motivates the users to skim through the text. Also, using bullet points is the only way your page can be shown in the Search engines results page as featured snippets like this!
Lastly, using defined headings in a particular layout as in this blog also enhances readability.
c. Load time
Load time is the time it takes for your web page to launch fully. It is very significant to your website. It does not mean if your web server was down for an hour and you will lose your rankings. But imagine, if every time people who come to your website click back because your site took too long to respond, will Google like this factor of your website?
It depends on many factors. Unused JavaScript and CSS files, or large-sized images in high definition or videos.
You can run a speed test that tells how fast or how slow your web page loads. It also tells you what things went right and what are the things that you can improve to make your website load faster. You can then take these suggestions to your developer, in case you are not able to do that by yourself.
For images, you can compress the images in a way that does not ruin their view quality but still reduces their size.
For videos, you can try embedding the videos instead of putting them on your website. For example, you can upload your video to YouTube and then using the embed option in your CMS, you can embed it on your content. This way, the server load for that long video is not put on your web page. YouTube handles that for you.
3. Other important SEO On-Page techniques
a. Links
Links are the stepping stones for search engines. Search engines apart from their natural crawling process, discover new web pages on the internet through links.
So, as a good citizen of the internet, you should consider giving links.
There are two types of links:
One, Internal links which you provide to link the pages of your own website. They transfer relevant traffic and also help search engines know that your website has topical authority over what you offer.
Second, External links, which you give to other websites. They also
transfer valid traffic, leads to a good user experience and also hints the search
engines know that the site is linked to have good authority over the
subject being talked about.
Voila!
So, that is all you have in 2022 concerning the On-Page search engine optimization
checklist to keep in mind for the next time you want to optimize your web pages
or while updating new ones.
If you have any questions, feel free to drop them in the comments below or reach me out through the contact us form embedded in the sidebar.
A friend might need this information, share it.
You think I should improve somewhere; you can mention that in the comments too.
I am Pawan! Thank you for reading!






1 Comments
Thanks for providing information about digital marketing this blog helps everyone who wants to know about digital marketing. If you're looking for Digital Marketing Services in Gurgaon click on the website URL now.
ReplyDelete